Week 6
Calibrating an Ultrasonic Distance Sensor (HC-SR04 / RCWL-9610) with an Arduino.
Ultrasonic Sensor Calibration
This week, I focused on calibrating an ultrasonic distance sensor, specifically the HC-SR04 (sometimes labeled as RCWL-9610). My goal was to measure known distances and compute linear regression coefficients (a and b) to correct the sensor’s output. The sensor is connected to an Arduino Uno, and a simple pushbutton is used to capture calibration data points.
Below is a table describing the pin connections between the Arduino Uno and the HC-SR04:
| Arduino Uno Pin | Sensor Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D9 | TRIG | Digital output to trigger the ultrasonic pulse. |
| D10 | ECHO | Reads the echo pulse width, used to calculate distance. |
| 5V | VCC | Powers the sensor (5 V supply). |
| GND | GND | Common ground connection for the sensor and Arduino. |
| D2 | Button | Pushbutton input for capturing calibration distances. |
In the code, BUTTON_PIN is configured with INPUT_PULLUP,
so one side of the pushbutton goes to Arduino pin D2, and the other
side goes to ground. This way, pressing the button pulls the pin low.
Here is the circuit diagram for the setup:
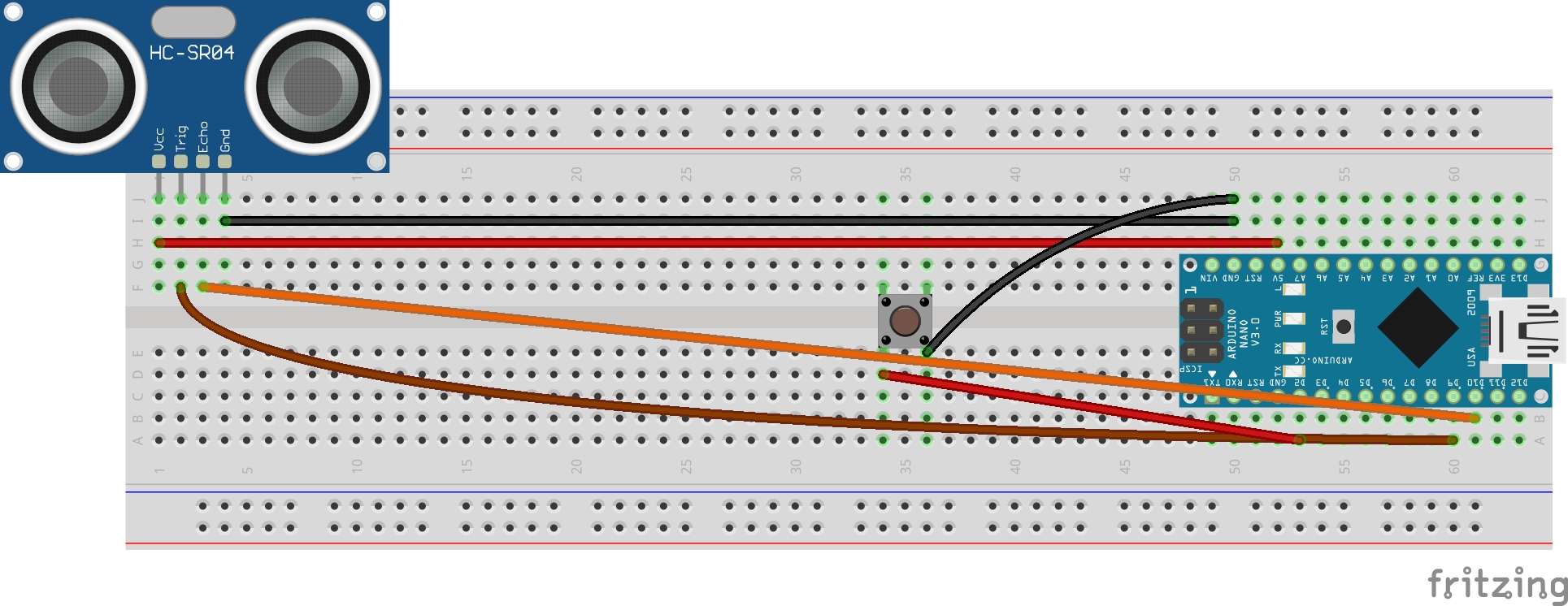
Once connected, pressing the button stores a sensor reading for a known distance. After multiple points (e.g. 10 cm, 20 cm, 40 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm), the code calculates the best-fit line and applies the correction. That lets me see more accurate distances when an object is placed in front of the sensor.

Below is the Arduino code I wrote, which measures distance, prompts for each calibration step, then computes the linear correction factors to compensate for the sensor’s inherent inaccuracies.
#define TRIG_PIN 9
#define ECHO_PIN 10
#define BUTTON_PIN 2
const int numPoints = 5;
int calibrationIndex = 0;
bool calibrated = false;
// Known real distances for calibration (in cm)
float realDistances[numPoints] = {10, 20, 40, 80, 100};
float measuredDistances[numPoints];
// Calibration coefficients (computed later)
float a = 1.0, b = 0.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(TRIG_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ECHO_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
Serial.println("=== Calibration Mode ===");
Serial.print("Place object at ");
Serial.print(realDistances[calibrationIndex]);
Serial.println(" cm and press the button.");
}
void loop() {
if (!calibrated) {
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW) {
delay(200); // debounce
float measured = measureDistance();
measuredDistances[calibrationIndex] = measured;
Serial.print("Value saved for ");
Serial.print(realDistances[calibrationIndex]);
Serial.println(" cm.");
calibrationIndex++;
if (calibrationIndex >= numPoints) {
computeCalibration();
calibrated = true;
Serial.println();
Serial.println("=== Calibration Complete ===");
Serial.print("Slope (a): ");
Serial.println(a, 4);
Serial.print("Intercept (b): ");
Serial.println(b, 4);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Now continuously scanning (corrected values):");
Serial.println();
} else {
Serial.print("Place object at ");
Serial.print(realDistances[calibrationIndex]);
Serial.println(" cm and press the button.");
}
while (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW); // wait for release
}
} else {
float raw = measureDistance();
float corrected = a * raw + b;
Serial.print("Corrected distance: ");
Serial.print(corrected);
Serial.println(" cm");
delay(500); // Adjust scan speed
}
}
float measureDistance() {
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
long duration = pulseIn(ECHO_PIN, HIGH);
return duration * 0.0343 / 2.0; // Convert microseconds to cm
}
void computeCalibration() {
float sumX = 0, sumY = 0, sumXY = 0, sumX2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; i++) {
float x = measuredDistances[i];
float y = realDistances[i];
sumX += x;
sumY += y;
sumXY += x * y;
sumX2 += x * x;
}
a = (numPoints * sumXY - sumX * sumY) / (numPoints * sumX2 - sumX * sumX);
b = (sumY - a * sumX) / numPoints;
}Calibration in Action
Here is a short demonstration video of the ultrasonic sensor calibration: